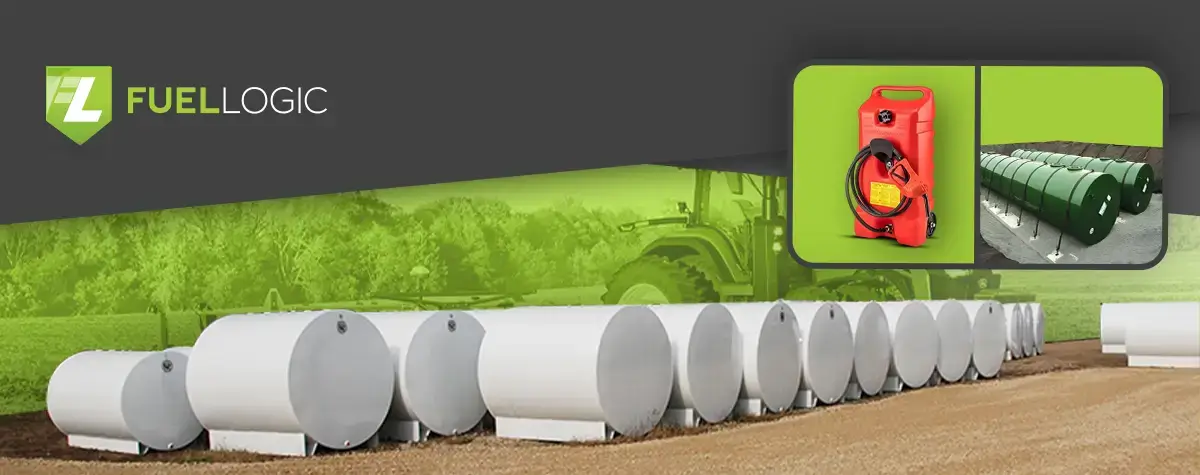
As the demand for efficiency grows, consumers, especially farmers, seek ways to save time. Farmers want to spend more time working in their fields to make more money, so they’ve been using bigger equipment to get their work done faster. Eventually, they need more giant fuel tanks to keep these larger machines running, which is why there is a growing demand for farm fuel tanks. If you are a farmer, knowing the different types of fuel storage tanks for farms is vital for your business.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
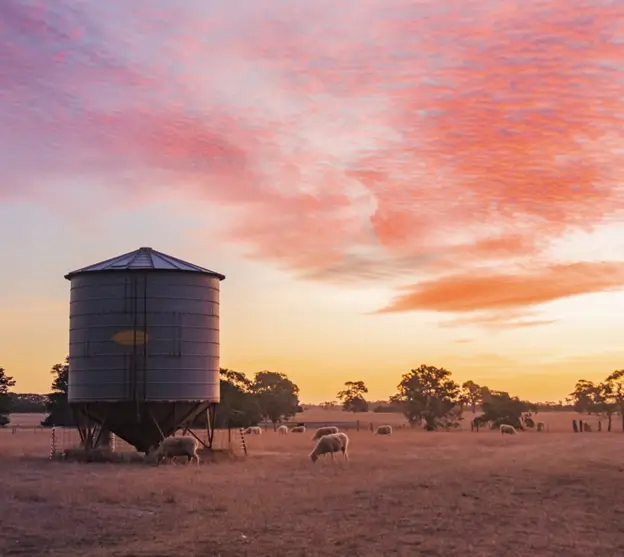

Fuel storage tanks for farms are crucial for agricultural operations. They provide a reliable and convenient fuel storage source for various equipment and machinery. They store and dispense fuel efficiently and ensure uninterrupted farm operations.
In this article, we will explore farm fuel tanks in detail, discussing their types, regulations, and the materials used in their manufacturing.
What is a Farm Fuel Tank?
Farm fuel tanks are containers used in farms to store fuel for agricultural diesel tank machinery and vehicles. These tanks are designed to hold fuel safely and efficiently so that farm operations run smoothly. The availability of farm tanks allows farmers to use agriculture fuel storage and other industry to easily access the fuel they need to power their farm equipment.
For example, diesel fuel is vital for tractors and other farm equipment. However, storing diesel can be tricky because it’s flammable. That’s where diesel fuel storage tanks for farm use prove invaluable.
Farm fuel tanks serve multiple purposes. They store gasoline, diesel, and other types of fuel used in farming. They can also store non-potable water, chemicals, and other farm supplies.
What are the different types of fuel storage tanks?
Fuel storage tanks for farms have various types, just like farms themselves. The tank you select depends on factors like your fuel consumption and the location of your farm. It also depends on the cost and frequency of fuel delivery, the size of your property, and other considerations.
The most common types of storage tanks used to store fuel are as follows:
Above Ground Fuel Tanks
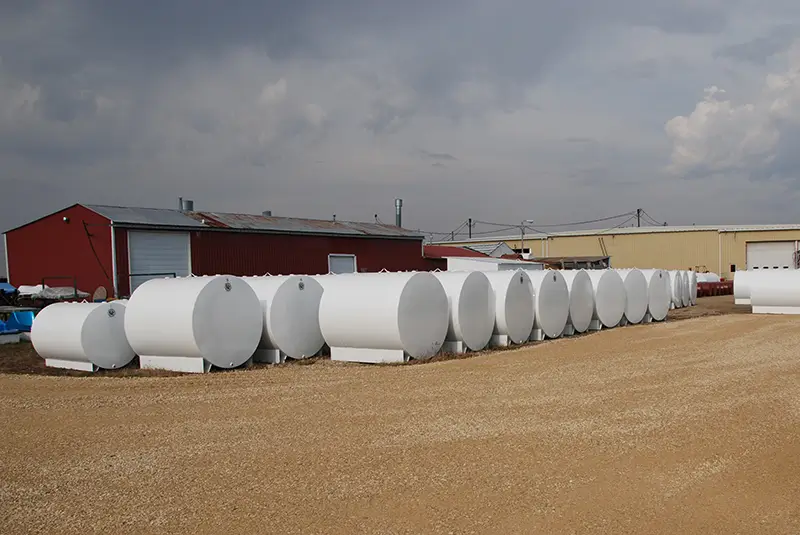

Above-ground fuel storage tanks are large containers placed on the earth’s surface. They are used for storing chemicals, crude oil, diesel exhaust fluid, gasoline, and other petroleum products in large quantities. These include overhead farm fuel tanks placed above ground, generally mounted on a platform or standing at a certain height. Above-ground fuel tanks are made of stainless steel, fiberglass, or polyethylene and placed on stable platforms.
An aboveground diesel fuel tank is built from high-quality materials to withstand different weather conditions. It is also bunded, which means it has a secondary containment to prevent leaks or spills.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Above-ground fuel tanks are generally more cost-effective to install, maintain, and repair because they don’t need any excavation or specialized equipment. | Above-ground tanks can face stability issues in severe weather conditions. |
| They have a longer lifespan than underground tanks as they are less prone to corrosion. | Regular monitoring of tank supports is required for safety assurance. |
| They do not require electric pumps since gravity feed can dispense fuel. | Above-ground tanks are vulnerable to fuel theft due to gravity feed systems. |
| You can effortlessly monitor fuel levels with above-ground tanks |
Underground Fuel Tanks
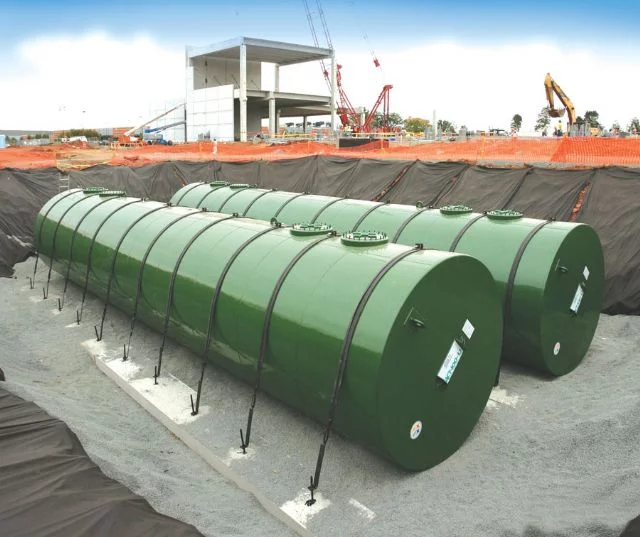

Underground Storage Tanks (USTs) are types of fuel storage tanks that store petroleum products, chemicals, and other hazardous materials beneath the ground. They are usually made of steel or fiberglass and can vary in size from small to very large. The depth of an underground storage tank depends on its type and purpose but is typically around 2 to 3 feet below the ground surface. The maximum depth allowed is twice the tank’s diameter or 23 feet, whichever is less.
Many farms prefer underground storage tanks because they are buried beneath the ground, making them less vulnerable to harsh weather conditions like cyclones. Below-ground fuel storage tanks for farms provide added protection against intense weather events.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| They are generally more protected than aboveground tanks due to their buried nature. | Higher upfront installation costs, planning intensity, and disruption compared to aboveground tanks. |
| Underground fuel tanks require a pump for fuel dispensing. To prevent fuel theft, turn off the power when not in use. | It is difficult to clean underground fuel tanks and detect potential leaks once installed. |
| Being underground frees up space for other essential equipment. | Once installed, you have limited flexibility in shifting the plant layout or relocating the tank. |
Portable Fuel Tanks
A portable fuel tank is a movable container used to store fuel safely. It ensures a convenient fuel supply to various locations. You can use them to transport fuel from your farm to wherever needed. For example, if your tractor runs out of fuel while ploughing a distant field, you can simply refill it using the portable tank.
Reliable portable fuel tanks include built-in safety features like flame arrestors, pressure relief valves, and secure locking mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. However, it’s crucial to recognize their limitations, as they may cause leakage problems if not properly maintained. Portable tanks may also have capacity restrictions and may not be suitable for long-term storage.
Materials Used in Fuel Storage Tanks
Fuel storage tanks are important for storing large fuel quantities, whether for commercial or personal use. Tanks are made of materials like steel, fiberglass, or plastic, each with unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right tank for your requirements.
Steel Tanks
Steel tanks are durable and can withstand harsh weather and damage from the outside. They also resist fire and explosions, making them the best industrial storage tanks. Even though they are more costly, their durability and longer lifespan often make them more cost-effective in the long run.
Fuel tank treatment, like cleaning and painting steel tanks regularly is essential to prevent rust. One downside is that recycling steel tanks is more challenging and may have a larger carbon footprint than plastic or other types of tanks.
Fiberglass Tanks
Fiberglass tanks are built using high-performance glass plastics and resin materials, known for their resistance to corrosion and heat. They’re popular for storing industrial chemicals and are well-suited for farm fuel handling and storage. The tanks’ walls, made with cross-filament winding technology, are solid.
Above-ground fiberglass tanks are not suitable for storing flammable liquids due to the resin used in their construction, which can catch fire. So, as per OSHA’s 1910.106(b)(1) standard, using above-ground fiberglass tanks for storing Class I, II, and IIIA flammable and combustible liquids is prohibited. However, you can use below-ground fiberglass tanks to store these flammable liquids.
OSHA may also permit the use of above-ground fiberglass tanks to store certain combustible liquids, like crude oil, but only in specific situations, like remote rural areas. These tanks must also meet the safety standards set by the National Fire Protection Association.
Plastic and Polyethylene Tanks
Polyethylene tanks, or plastic fuel tanks, are made from a special grade of plastic called High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE). This material is solid, durable, and reliable. Plastic tanks are lightweight, so they are easy to transport and install. Furthermore, they are generally more affordable than steel tanks because plastic is a cheaper material to produce.
Plastic tanks are also less likely to develop leaks, reducing the risk of contamination. However, they are more susceptible to damage from UV exposure, extreme temperatures, and harsh weather conditions. So, you must adhere to its safety guidelines to protect the tank from any harm.
Regulations and Compliance for Farm Fuel Tanks
Operating a farm fuel tank setup requires compliance with local and federal regulations for safer fuel storage. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and EPA state these regulations for local fuel storage.
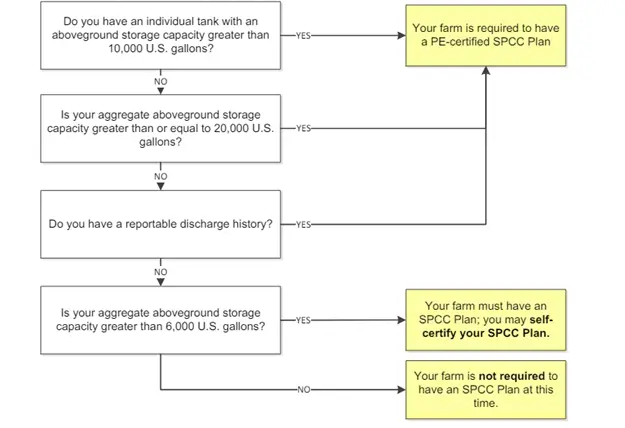
In addition, environmental considerations and impact assessments are also necessary for farm fuel tanks due to their potential risks to the environment and surrounding ecosystems. Therefore, the Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) regulation, part of the Federal Water Pollution Control Act (FWPCA), aims to stop oil spills from farms reaching waterways or shorelines.
If a farm stores, uses, or moves oil like diesel, gasoline, or vegetable oil and keeps more than 2,500 gallons in aboveground tanks, it must create and follow an SPCC Plan. This plan might need approval from a professional engineer, or the farmer can approve it themselves. Moreover, if a farm stores over 1,000,000 gallons of oil or more and has specific risks, or if it stores over 42,000 gallons and transfers oil to or from ships, it must make a Facility Response Plan and give it to the EPA.
For a better understanding, please refer to this flowchart:
FAQs
What size are farm fuel tanks?
Farm fuel tanks are commonly available in sizes such as 275, 500, and 1,000 gallons, but larger options up to 30,000 gallons or more also exist. The size you choose depends on factors like your farm’s fuel usage, the fuel you use, and how often you need to refill.
How do you store gasoline on a farm?
Generally, gasoline is stored in farm fuel tanks on farms as a safety measure. Many people prefer this method for storing fuel safely. However, some also opt for small containers to store 50 to 200 litres of fuel.
How much does a fuel tank container cost?
The cost of a fuel tank container can vary depending on its size, material, brand, and any extra features. However, an above-ground fuel tank with a capacity of 3000 gallons costs approximately $5000.
What are the other types of fuel storage tanks?
There are various types of fuel storage tanks available to meet different needs. These include horizontal tanks, fixed roof tanks, cylindrical fuel tanks, floating roof tanks, corrugated steel tanks, rigid removable fuel tanks, and septic tanks.
Conclusion
The agricultural industry is the backbone of any country’s economy because it contributes significantly to state revenue. Therefore, choosing the appropriate fuel storage tank is crucial for farm operations, ensuring safety, compliance, and efficiency. We have already discussed different types of farm fuel tanks and highlighted their construction materials.
However, if you need expert guidance on maintaining your fuel storage tank and managing fuel deliveries via effective route planning management, consult us here in Fuel Logic. Fuel Logic is your trusted fuel delivery partner, just a call away. If you need to refill your fuel tanks at your farm or even for your onsite construction fuel tanks, simply order fuel from us, and we will deliver the required fuel to your farm location using our efficient mobile fueling as soon as possible. Trusting Fuel Logic is a high-return investment that will provide you with quality fuel storage solutions, offering long-term benefits for your farm’s operations.






