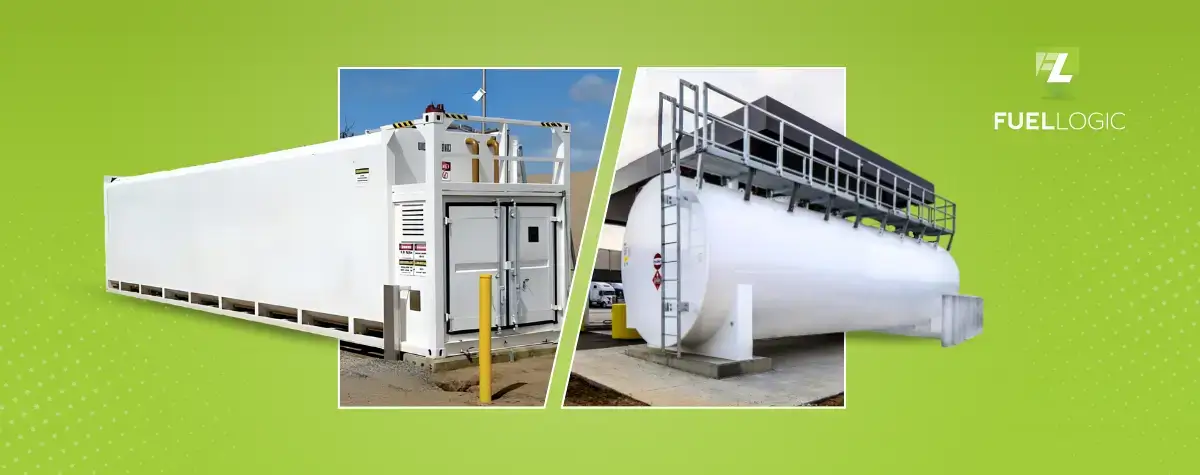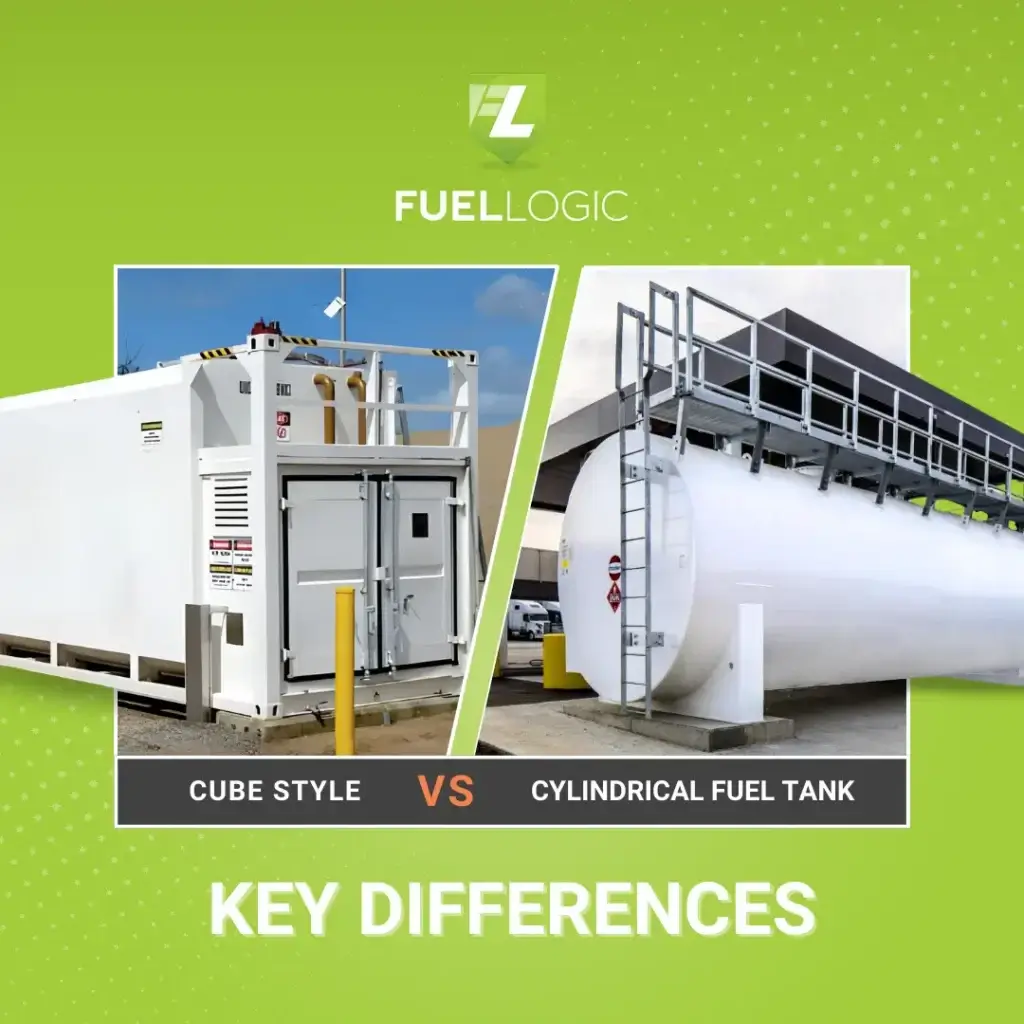
Selecting the right fuel tank is crucial for various applications as it directly impacts efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. When comparing cube style or cylindrical fuel tanks, several factors come into play, with considerations such as space, cost, and specific usage requirements playing a significant role.
Although cylindrical tanks are being predominantly used in the industries, cube fuel tanks are making their place in the market through their modern design, versatility, and efficient nature.
Whether you choose cube style or cylindrical fuel tank, the decision should be based on a thorough assessment of these factors in relation to the particular application.
What are Cube Style Fuel Tanks?
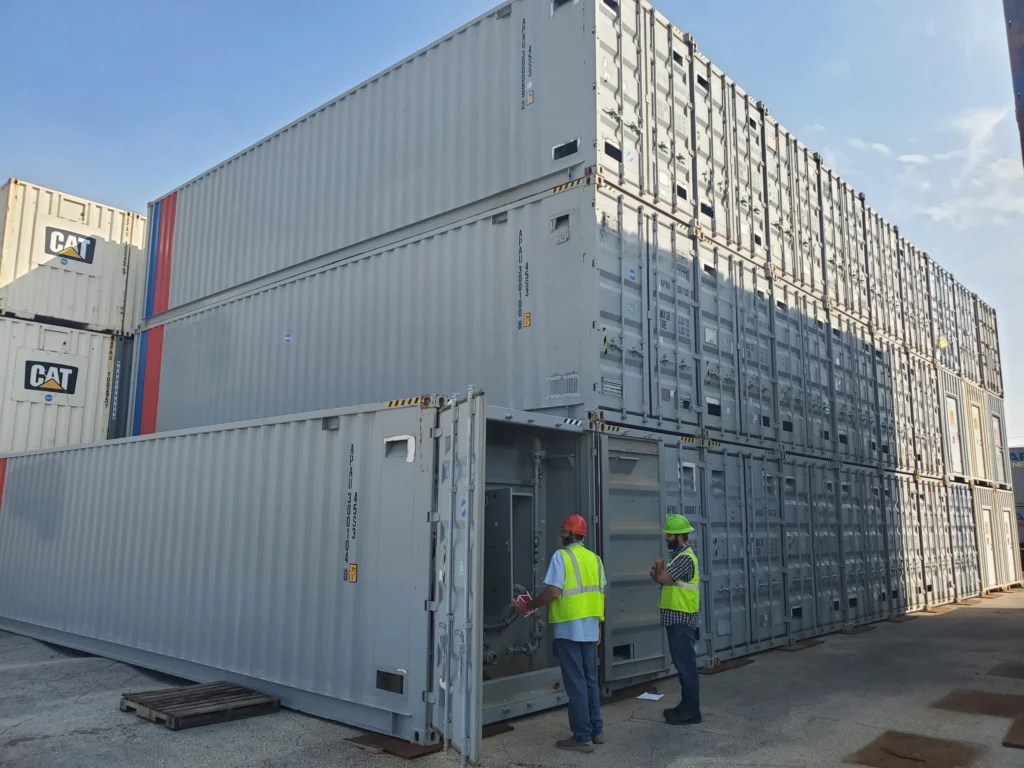

Cube fuel tanks are characterized by their cubic or rectangular prism shape. Steel, aluminum, or composite materials are commonly used for their construction, providing strength and durability.
The tanks usually have access points, including openings for filling, vents, and outlets. These are strategically placed for ease of use and efficient fuel management.
Cube fuel tanks are often employed in backup power systems, such as generators for commercial buildings or data centers. Their modular design facilitates easy integration with generator systems.
Common sizes of cube fuel tanks range from a few hundred to several thousand gallons where they find application in a variety of industries, including:
- Telecommunications
- Data Centers
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Emergency Power Systems
- Agriculture
Advantages of Cube Style Fuel Tanks
While there are some rules to follow in using cube fuel tanks, they prove to be a flexible and efficient choice for various modern uses.
Enhanced Security Features
Many cube fuel tanks are designed with lockable cabinets that house crucial components like fuel dispensing systems, control panels, and access points.
They may also incorporate integrated locking mechanisms for the main access points, such as fill ports, vents, and dispensing outlets.
These locking systems prevent tampering and unauthorized access to the fuel storage system.
Stability and Environmental Safety Benefits
Cube fuel tanks typically have a broad base that evenly distributes the weight of the fuel throughout the tank. In sensitive ecological areas, where the impact of spills can be severe, the stability of cube tanks is crucial.
Space-Saving Design and Efficiency
Cube fuel tanks have a smaller footprint compared to traditional cylindrical tanks of similar capacity. The ability to install these tanks in confined spaces makes them suitable for fuel storage in city centers or small industrial facilities where available area is limited.
Stackability for Optimal Space Utilization
Cube fuel tanks, with their cubic or rectangular prism shape, are inherently designed to be stackable. This design allows them to be safely and efficiently stacked vertically, maximizing the use of available vertical space.
Ease of Maneuverability with Forklift Pockets
Forklift pockets are often integrated into cube fuel tanks to facilitate easy loading and unloading of cube tanks onto transport vehicles.
This is particularly beneficial in environments where the arrangement of fuel storage may need to be adjusted based on changing operational needs.
What Are Cylindrical Fuel Tanks?
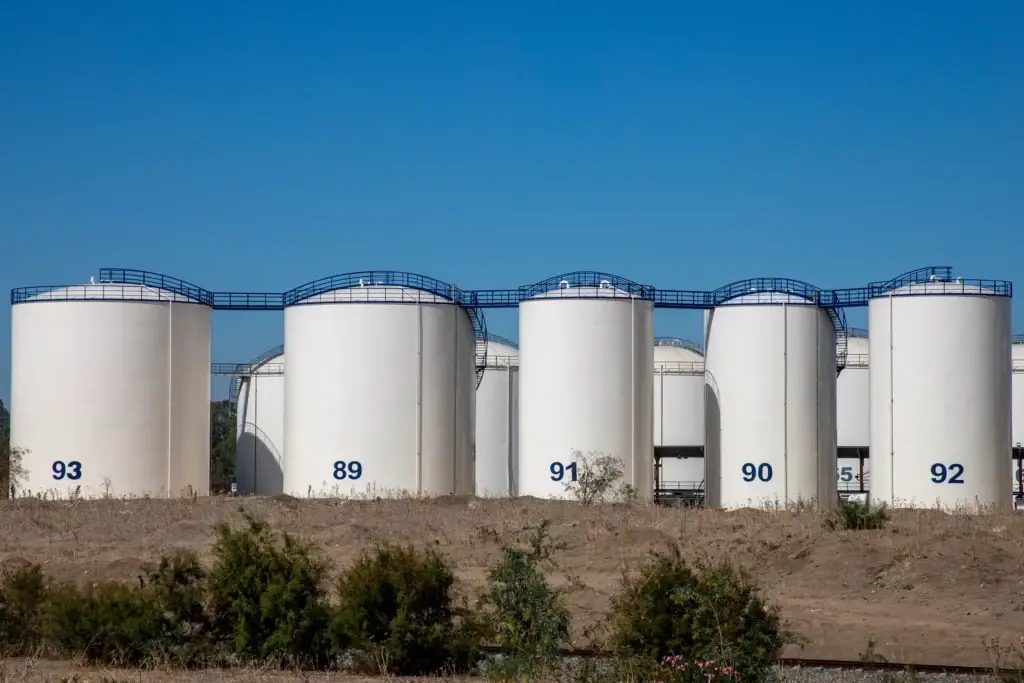

Cylindrical Fuel Tanks represent a traditional and widely used design for storing and transporting fuels. Their cylindrical shape, characterized by a curved or straight sidewall and circular cross-section, has been a standard in fuel storage for various applications.
Their design, rooted in historical military and aviation applications, has stood the test of time, making them a standard choice in the fuel storage industry.
The fuel tanks have been prevalent in residential heating systems, serving as storage vessels for heating oil in homes. This traditional role dates back to the widespread adoption of oil-based heating systems.
Advantages of Cylindrical Fuel Tanks
Despite evolving technologies, the enduring design of cylindrical tanks continues to make them a go-to solution for efficient fuel storage in diverse industrial applications.
Cylinder fuel tanks are integral to manufacturing processes, supporting the fueling needs of machinery and equipment in factories and industrial facilities.
1.Cost Effectiveness Compared to Cube Style Tanks
Cylindrical tanks often use materials that are readily available and cost-effective, such as steel or aluminum.
The long-standing use and widespread adoption of cylinder tanks have led to standardized manufacturing processes. The materials, combined with the straightforward cylindrical design, contribute to a lower overall manufacturing cost.
2. Durability and Longevity in Harsh Conditions
Cylindrical tanks are commonly constructed using robust steel alloys. To enhance durability, the tanks often feature corrosion-resistant coatings.
Thanks to their sturdy design and weather-resistant finishes, cylinder fuel tanks can endure extreme weather conditions, including heavy rain, snow, and high winds, without compromising their performance.
3. Versatility in Storage and Transportation
Cylinder gas tanks are suitable for storing liquid gasses, such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG).
Cylindrical tanks are also well-suited for railcar transportation, providing an effective solution for moving large volumes of liquids or gasses over long distances.
The tanks are commonly used for transporting fuels, chemicals, and other liquids over short to medium distances. The cylindrical shape allows for efficient placement and secure attachment to truck trailers.
4. Familiarity and Widespread Availability in the Market
The prolonged use of cylindrical tanks has led to the standardization of components and manufacturing processes. This standardization facilitates compatibility between different tank models, making it easier for users to find replacement parts or components when needed.
The familiarity with cylindrical tanks leads to predictable and standardized maintenance procedures by operators and maintenance personnel.
Cube Style Vs. Cylindrical Tanks
Factors | Cube Fuel Tanks | Cylindrical Fuel Tanks |
| Storage Capacity | Available in a range of sizes, from small to large capacities. Larger volumes can be achieved with modular stacking. | Offer a variety of capacities, from small to very large. Adaptable design allows for scalability, making them suitable for diverse storage requirements. |
| Space Requirements | Compact design optimizes both horizontal and vertical space. Well-suited for locations with limited ground area, such as urban settings or small industrial sites | Efficient use of vertical space.Adaptable to various layouts, especially where vertical space is more readily available than horizontal space. |
| Mobility | Easily maneuverable with features like forklift pockets.Suitable for temporary or mobile applications, offering flexibility in placement. | May require specialized equipment for movement. It is commonly used for fixed installations but can be transported efficiently using trucks, railcars, or ships. |
| Maintenance | Modular design allows for easy inspection and maintenance. Accessible components contribute to straightforward upkeep. | Familiarity with maintenance procedures due to long-standing use. Standardized components ease repairs, and spare parts are readily available. |
| Environmental Safety | A stable design reduces spillage risks. Tamper-evident features contribute to environmental safety. | Stable construction minimizes the risk of tipping over. Commonly used for fuel storage in a manner that minimizes environmental impact. |
| Adaptability | Versatile placement options, adaptable to varied environments.Suitable for both permanent installations and temporary projects. | Adaptable to different applications and industries. Proven versatility in storage and transportation, well-suited for various liquids and gasses. |
| Security | Often equipped with lockable cabinets and integrated locking mechanisms. Tamper-evident features may enhance security against theft or unauthorized access. | Security features may vary but can include lockable access points. Generally secure but may require additional measures for enhanced protection. |
Cost Considerations and Long-Term Investment
The choice between cube style or cylindrical fuel tanks involves weighing initial costs against long-term benefits.
1. Initial Purchase Costs
Generally, cube fuel tanks may have a higher initial purchase cost compared to cylindrical tanks due to their modern design, additional features, and materials. The cost can vary based on the size, materials, and any specialized features (e.g., security measures).
2. Installation Costs
Cube fuel tanks are often designed for easy installation, utilizing features like forklift pockets. Generally, installation costs may be lower due to the ease of handling.
Installation costs of cylinder fuel tanks may vary depending on factors like size, accessibility, and any site-specific requirements and may require specialized equipment for handling, potentially adding to installation expenses.
3. Maintenance Costs
Cube fuel tanks have a modular design that facilitates easier inspection and maintenance. Standardized components and modern features may contribute to lower maintenance costs.
However, standardized components of cylinder fuel tanks make repairs straightforward, potentially reducing maintenance expenses.
Key ROI Factors
- Fuel Storage Efficiency: Consider the ability of each tank type to efficiently store fuel based on the available space and required capacity.
- Security Features: Assess the importance of security features in minimizing theft or unauthorized access, which may impact long-term costs.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Evaluate the expected maintenance and repair costs over the tank’s lifecycle, considering ease of servicing and availability of spare parts.
- Adaptability to Changing Needs: Consider the adaptability of the tank type to evolving requirements, expansions, or changes in fuel storage needs.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Both cube style or cylindrical fuel tanks can be designed to meet environmental impact and safety regulations.
Cube fuel tanks often incorporate features that minimize environmental impact, such as secondary containment systems to prevent spills.
Cylindrical tanks and their environmental impact may be influenced by factors like the tank’s location, maintenance practices, and the use of safety features. Compliance may be facilitated by standardized components and well-understood maintenance procedures.
Customization and Additional Features
Both fuel tanks for diesel can be customized with various coatings such as corrosion-resistant coatings, UV-resistant finishes, and coatings that facilitate easy cleaning.
Custom fittings include specialized fittings for fuel dispensing, overfill prevention systems, and additional ports for monitoring equipment.
Cube fuel tanks often support advanced monitoring systems. These systems can include sensors for fuel level monitoring, leak detection, RFID access controls and remote monitoring capabilities.
Cylinder fuel tanks may involve adding level sensors, temperature sensors, and integration with telemetry systems to enable remote monitoring and data collection.
However, to work properly, these tanks require regular cleaning and treatment for their efficient functioning, so make sure to employ a method most suitable for your fuel tank.
Industry Specific Recommendations
Both cube style or cylindrical fuel tanks can prove to be viable choices for various industries.
Agriculture: This includes the agriculture industry, where cube fuel tanks are ideal for temporary setups, easy maneuverability, and space efficiency in farmyards, while cylindrical tanks are more suitable for more permanent settings, due to their adaptable nature and robust construction.
Construction: For the construction industry the choice of your tank depends on the size of your set-up, where cube fuel tanks are ideal for saving up space, mobility on-site thanks to their forklift feature, and advanced monitoring systems to scale up your security.
Cylindrical tanks have proven their reliability on construction sites, with their compatibility with different fuels and durability in harsh conditions.
Cube fuel tanks are mobile for use at transport hubs, stackable for efficient storage, and have fittings for easy integration with transport vehicles. Cylindrical tanks are more suited for fixed installations at transportation depots, stable for safe fuel storage, and also comprise fittings for efficient fuel transfer.
Within the aviation industry, cube fuel tanks are known for their compact structure and mobility in airport settings. The advantage cylinder fuel tanks have over cube fuel tanks, mainly lies in their familiarity with the industry as well as their versatile nature to support various aviation fuels.
Reliable fuel supply is the lifeblood of many industries. It underpins operational efficiency, cost management, regulatory compliance, and overall resilience, contributing to the long-term sustainability and success of businesses in diverse sectors. Fuel Logic offers comprehensive fuel supply solutions tailored to diverse industries, providing insights into optimal fuel storage choices.
Conclusion
The correct fuel tank aligns with the unique needs of each industry, contributing to seamless operations and long-term success.
Businesses should conduct a thorough assessment of their fuel storage requirements, considering industry specifics, space constraints, and usage patterns. Consult with fuel supply experts like Fuel Logic to gain industry-specific insights and recommendations.
And remember, the right fuel tank is not just a container; it’s a strategic asset that can significantly impact the success of businesses across various industries.
FAQs
1. What are the main differences between cube style and cylindrical fuel tanks?
The primary distinctions lie in their design and structural specifics. Cube fuel tanks are modular, space-efficient, and easily maneuverable, while cylindrical tanks are traditionally stable, robust, and adaptable to various fuels.
2. Are cube style fuel tanks more expensive than cylindrical tanks?
Cube fuel tanks can be more expensive than cylinder fuel tanks due to their modern design and features.
3. Which fuel tank type is safer for the environment?
Both tank types can be designed with environmental safety in mind. Cube fuel tanks may offer features like spill containment, while cylindrical tanks can have coatings to resist corrosion, contributing to environmental safety.
4. Can cube style fuel tanks be stacked?
Yes, cube fuel tanks are designed for efficient space usage and can be stacked, maximizing vertical storage space. This feature is particularly valuable in high-density storage areas.
5. What are the typical uses of cylindrical fuel tanks?
Cylindrical tanks find application in various industries, including agriculture, construction, transportation, mining, marine, and aviation. Their stability and adaptability make them suitable for on-site storage and fixed installations.
6. How do I choose between a cube style and a cylindrical fuel tank for my needs?
Consider factors like industry requirements, available space, mobility needs, and environmental conditions. Evaluate the advantages of each type, such as stackability for cubes and stability for cylindrical tanks, to make an informed decision aligned with your specific needs.





