Fuel management is a critical aspect of running a successful construction site. From heavy machinery to generators, fuel powers our operations and keeps projects on track.
However, construction site refueling involves navigating safety hazards, environmental concerns, and potential disruptions to project timelines. Moreover, the on-site storage of fuel, while convenient, is bound by strict regulations and standards. Improper handling and storage can lead to significant risks, including fire hazards, property damage, and even fatalities.
In this guide, we’ll address these complexities, offering smart and efficient strategies for refueling on construction sites to avoid common mistakes.

Understanding the Importance of Safe Refueling in Construction Sites
Unsafe refueling can have dire consequences. For instance, if diesel fuel is mishandled, it can lead to fires or explosions. Such incidents not only endanger lives but can also cause significant project delays and financial losses. Another risk is environmental contamination due to fuel spills.
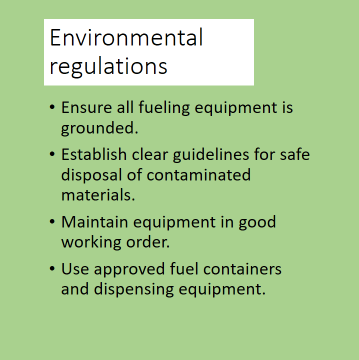
Compliance and Training
Compliance with OSHA regulations is crucial to safe refueling practices in construction sites. Here are some key OSHA guidelines that apply:
- Only approved containers and portable tanks should be used for storing and handling flammable liquids. Specifically, for handling flammable liquids in quantities of 5 gallons or less, approved safety cans or Department of Transportation-approved containers are required.
- When transferring flammable liquids in quantities greater than 5 gallons, the area must be at least 25 feet away from other operations or protected by fire-resistant construction.
- Transferring Category 1, 2, or 3 flammable liquids from one container to another must be done only when containers are electrically interconnected, which helps prevent static electricity, a potential ignition source.
- Flammable liquids should only be drawn from or transferred into containers through a closed piping system, safety cans, or approved valves. Using air pressure for transferring is strictly prohibited.
- Flammable liquids should be stored in approved closed containers or tanks, either underground or in aboveground portable tanks. Additionally, dispensing hoses and nozzles must meet safety standards.
- There must be clearly identified and easily accessible switches at a location away from dispensing devices. These are for shutting off power to dispensing devices in emergencies.
Ongoing training for personnel is equally important. It’s not just about following regulations; it’s about ingraining safety as a habit. Training should cover efficient fueling practices and critical safety protocols, including proper handling of fuel and emergency response procedures for spills or fires.
Mitigating Fuel Spillages
Mitigating fuel spillage impacts that extend across financial, environmental, and safety realms. Financially, fuel spillages can be quite costly, not just due to the need for extensive clean-up efforts but also because of potential fines arising from regulatory non-compliance.
From an environmental standpoint, spills are particularly detrimental, as they contaminate soil and water, causing harm to local ecosystems. Safety-wise, the consequences of spillages are equally serious. They pose severe fire hazards in areas crowded with machinery and personnel, increasing the risk of injuries.
To effectively prevent fuel spillages during construction site refueling, several key strategies should be employed.
- On-Site Fueling: Choosing on-site fueling mitigates the risk of spillages that can occur during transportation. This method ensures that refueling is conducted in a controlled environment.
- Regular Equipment Servicing: To prevent spillages, it’s vital to maintain equipment regularly. Ensuring that all machinery is in prime condition reduces the likelihood of leaks and malfunctions that could lead to fuel spillages.
- Crew Training: Educating your crew on efficient and safe fueling practices is essential. Training should include emergency procedures for managing spillages.
- Mark Refueling Areas: Designating specific areas for refueling helps in avoiding accidents. This organization aids in managing the movement of equipment and personnel in these high-risk zones.

Optimal Location for Fuel Storage
Choosing the optimal location for fuel storage on construction sites is crucial for safety and regulatory compliance. The OSHA primarily governs the guidelines for fuel storage placement under 29 CFR 1926.152(a) and 1917.156(b)(4). Here are the regulatory requirements to take note of:
- Only approved containers and portable tanks should be used for storing and handling flammable and combustible liquids.
- Stored fuel containers must be situated in areas that minimize exposure to high temperatures and physical damage.
- Containers should not be stored near exits, stairways, or areas intended for egress.
- Outlet valves of containers in storage or transport must be closed, and relief valves should connect with vapor spaces.
Incorrect storage of materials, particularly fuel, poses various risks. Fire hazards can arise if fuel is stored near heat sources or busy areas. Storing containers near exits or evacuation routes can block emergency escape, posing a major safety risk. Additionally, improper storage may cause environmental contamination through spills or leaks, impacting soil and groundwater.
Store fuel away from equipment or areas that generate heat and choose areas less likely to experience vehicle traffic, falling objects, or other forms of physical impact.

Safe Refueling Practices on Construction Sites
Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure safety during construction site refueling:
- Before starting, inspect the fuel tank, hoses, nozzles, and valves for any signs of damage or wear. This ensures everything is in good condition to avoid leaks.
- Make sure the refueling area is free of any obstructions. This minimizes the risk of accidents.
- Properly ground and bond the equipment to prevent static electricity, which can be a potential ignition source.
- Personnel involved in refueling should wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves and eye protection.
- After refueling, securely close the fuel cap and ensure that spills are cleaned immediately and safely.
- Keep records of the refueling process, including the amount of fuel used and any incidents that occurred.
During construction site refueling, adhering to refueling on construction site regulations is critical for safety. The use of appropriate safety equipment and protocols is a fundamental aspect of this process.
Essential Equipment and Materials
For efficient refueling, the right equipment and materials are essential. This includes sturdy fuel tanks, modern fuel pumps, and dispensers.
Safety cans are important for handling smaller fuel quantities, especially flammable liquids, safely. In case of accidental spills, spill containment kits, which include absorbents and barriers, are indispensable for quick and effective cleanup.
Significant advancements have been made in this field. Fuel storage now often involves double-walled tanks with advanced leak detection systems. Dispensing systems have been upgraded with features like automatic shut-off and digital flow meters for better accuracy.

Best Practices for Construction Site Refueling
Best practices for construction site refueling focus on safety, efficiency, and environmental compliance. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Keep the refueling site clean and orderly. Ensure the tank cabinet or drip tray is emptied weekly to avoid spillages.
- It’s legally required to have a site drainage plan. This plan should detail where fuel will go in case of a spill.
- Use containment strategies to prevent contamination of areas like grass verges or waterways. Regularly maintain interceptors in refueling areas, ideally every six months.
- Consider remote monitoring for tanks and pumps. Regular testing of overfill alarm systems ensures they are in working order.
Implementing these best practices in construction site refueling enhances safety and efficiency and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
Innovative Solutions and Technologies
Modern technologies significantly enhance the safety and efficiency of refueling on construction sites. Automated fuel management systems are at the forefront of this revolution, offering precise control over fuel dispensing and minimizing risks of overfilling and spillage.
Remote monitoring technology is another game-changer, allowing for the off-site monitoring of fuel levels and system integrity. This capability is crucial for early detection of leaks or irregularities, ensuring immediate action even when no personnel are on-site.
Additionally, cloud-based reporting capabilities integrated into fuel management systems offer detailed insights into fuel usage patterns, enabling better planning and strategic decision-making.
Mobile refueling apps have also become an indispensable tool, allowing operators to efficiently track fuel delivery and consumption, schedule refueling activities, and receive timely alerts, all from their mobile devices.

Safety Measures and Risk Mitigation
Adhering to refueling on construction site regulations is crucial for safety and risk mitigation. Key practices include:
- Safety Protocols: Regular inspections of refueling equipment, proper fuel handling and storage, and the use of PPE are essential to prevent incidents.
- Emergency Plans: Prepared plans for spill containment, fire outbreaks, and first aid ensure a quick response to emergencies.
- Employee Training: Regular training in safe refueling practices and emergency responses helps employees stay prepared.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Using biofuels or electric-powered machinery can significantly lower carbon emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Emphasizing sustainability in construction fueling not only addresses environmental concerns but also often leads to cost savings and improved public perception of the construction industry. Implementing these eco-friendly strategies demonstrates a commitment to preserving natural resources for future generations.

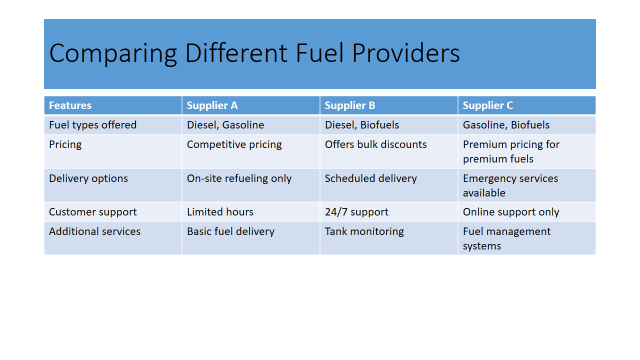
Choosing the Right Fueling Solutions Provider
Choosing the right fueling solutions provider is crucial for efficient and safe construction site operations. When evaluating different providers, consider these key factors:
- Look for providers with a strong reputation and proven track record in the industry. Experience in handling construction site refueling and proper route planning for your fleet is a must.
- Ensure the provider adheres to all relevant safety and environmental regulations.
- The quality of fuel supplied directly impacts machinery performance and efficiency. High-quality fuel can reduce maintenance costs and downtime effective for your fleet fueling.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the essentials of safe and efficient refueling on construction sites. Adhering to safety protocols, choosing eco-friendly fuels, and selecting the right fueling provider are crucial for operational success and sustainability.
For hassle-free fuel delivery, Fuel Logic is a reliable choice. Serving nationwide, we offer diesel, gasoline, and DEF directly to your site. With Fuel Logic, you’ll enjoy efficient, on-demand fuel services across the US. Contact us or use our online form for quick, reliable fueling solutions.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the primary risks associated with unsafe refueling on construction sites?
The primary risks include fire hazards, environmental contamination from spills, health risks from exposure to fuel vapors, and potential injuries due to improper handling of fuel.
What type of fuel does most construction equipment use?
Most construction equipment uses diesel fuel due to its efficiency, energy density, and suitability for heavy-duty machinery.
How do you store fuel on a construction site?
Fuel on construction sites should be stored in approved containers or tanks, in a secure, well-ventilated area, away from ignition sources, and with proper spill containment measures in place.
Why is the location of fuel storage crucial on construction sites?
The location is crucial to minimize fire risks, ensure easy access for refueling while avoiding high-traffic areas, and to comply with safety regulations regarding proximity to work areas and environmental protection.
What are the OSHA rules for fuel storage?
OSHA rules for fuel storage include using approved containers, keeping fuel away from exits and high-traffic areas, ensuring containers are properly labeled and secured, and implementing measures for spill control and fire safety.





